Introduction
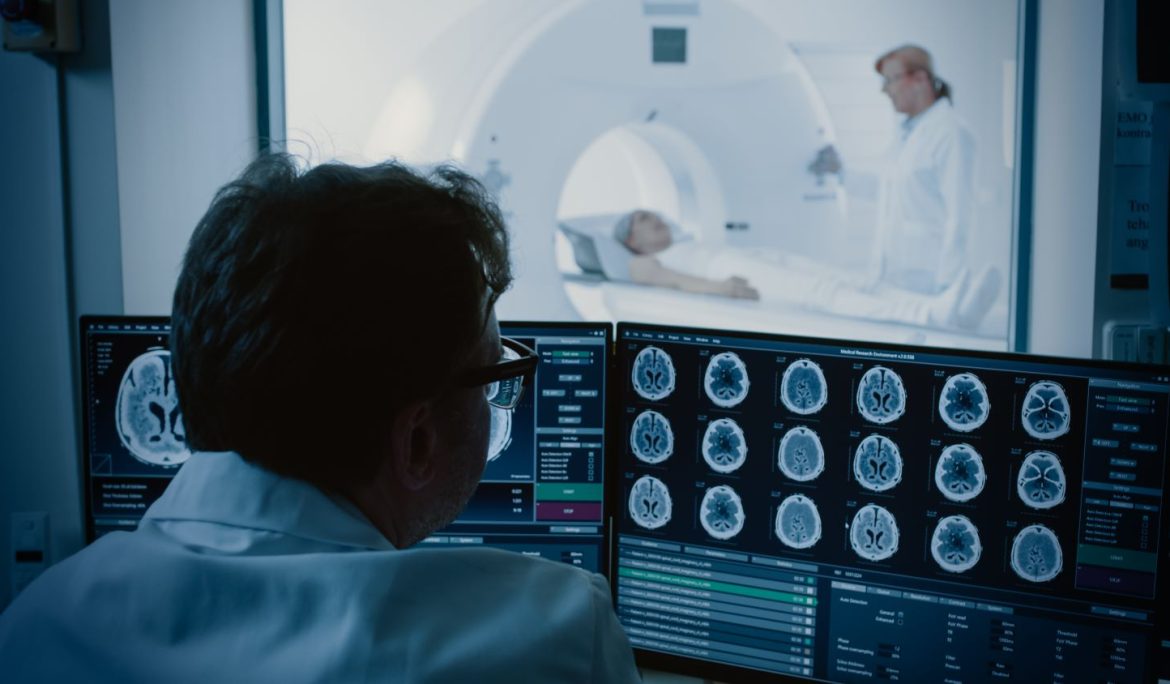
Interventional radiology (IR) is a subspecialty of radiology that utilizes imaging guidance to perform minimally invasive procedures. This innovative approach offers numerous benefits over traditional surgical methods, including reduced risk, shorter recovery times, and less discomfort for patients.
Common Interventional Radiology Procedures
nterventional radiologists perform a wide range of procedures, including:
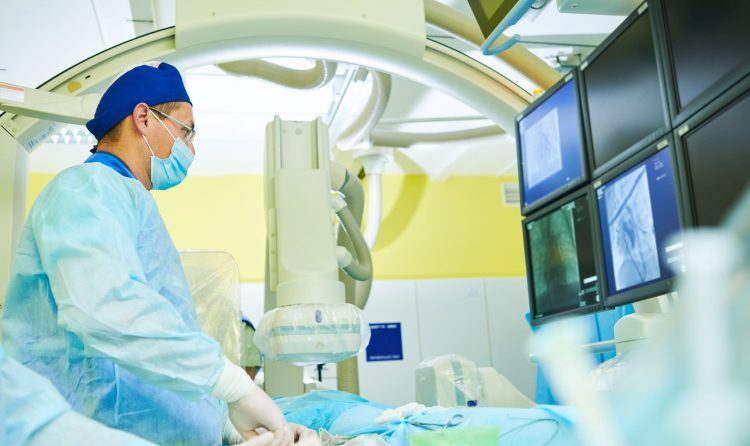
- Angioplasty and Stent Placement: Used to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels.
- Embolization: Involves blocking abnormal blood vessels to treat conditions like aneurysms or tumors.
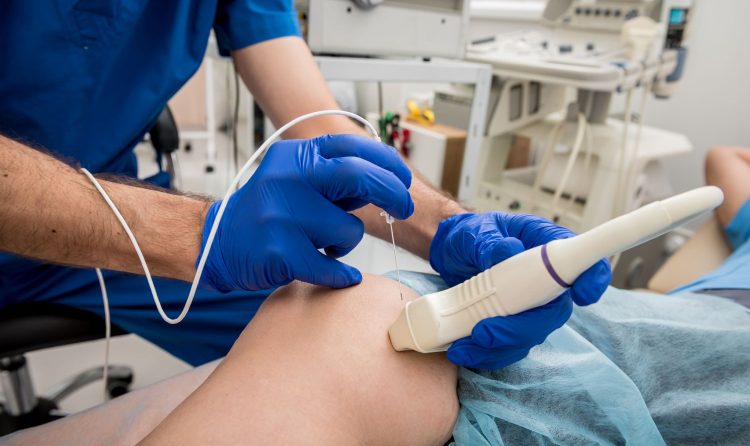
- Image-Guided Biopsies: Allows for precise sampling of tissue for diagnosis.
- Drainage Procedures: Used to drain abscesses or fluid collections.
Advantages of Interventional Radiology
The minimally invasive nature of IR procedures offers several advantages:
- Reduced Risk: Smaller incisions mean lower risk of infection and complications.
- Shorter Recovery Time: Patients often experience quicker recovery compared to traditional surgery.
- Less Pain and Discomfort: Minimally invasive techniques typically result in less postoperative pain and discomfort.
- Outpatient Options: Many IR procedures can be performed on an outpatient basis, reducing hospital stays and associated costs.
The Future of Interventional Radiology
As technology continues to advance, the scope and effectiveness of interventional radiology are expected to grow. Emerging techniques, such as robotic-assisted procedures and advanced imaging modalities, are likely to further enhance the precision and outcomes of IR treatments.